Overview Link to this section
Learning is a social activity for young children! They are exploring and making sense of the world through play and interacting with others. In the first five years of young children’s lives, they begin to learn the essential social and emotional skills of self-awareness, self-regulation, social and emotional understanding, empathy and caring, and how to build friendships and interact with others (CA Preschool Learning Foundations, Vol.1, 2008). Early childhood educators guide young children to develop the habits and tools to experience, express, and manage their emotions, establish positive and rewarding relationships with others, and make responsible decisions for themselves and towards others in culturally and developmentally appropriate ways. The five core social and emotional competencies of social and emotional learning are:
- Self-Awareness: Ability to recognize and name our individual emotions, strengths, and skills we are working on. Ability to identify the continuum of complex emotions.
- Self-Management: Ability to regulate our feelings and behaviors, persevering through challenges, and anticipating and choosing positive responses to situations.
- Social Awareness: Ability to understand others’ feelings and take their perspective. Ability to understand how moods, motivations, experiences, and knowledge affect our personal behaviors, as well as, others’ behaviors.
- Relationship Skills: Ability to develop positive relationships, manage conflict, and work collaboratively.
- Responsible Decision Making: Ability to make positive and constructive choices about personal behaviors and responses. Skills include problem-solving, reflection, perceptive thinking, self-direction, and personal motivation.
Priority Standards Link to this section
In Pre-K we focus on these critical areas:

Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is an important component of early school success because young children’s self-confidence shapes their interest, motivation, and persistence in academic work, and their success in the classroom reciprocally influences their sense of pride and accomplishment.

Self-Regulation
Self-regulation is relevant to the management of emotions and emotion-related behavior, attention, cognitive activity, and social behavior (such as impulses to act aggressively when provoked).

Social and Emotional Learning
Preschoolers who are more socially and emotionally perceptive are capable of greater success in their relationships with peers and adults which is relevant to school readiness.

Empathy and Caring
A young child's capacity to respond sympathetically and help fully to others in distress is built on children’s developing social and emotional understanding and contribute to their ability to cooperate successfully with others in group learning environments.

Initiative in Learning
How children approach new learn ing and problem-solving challenges is a critical feature of their academic success. “Approaches to learning” is an important predictor of classroom achievement in kindergarten and the primary grades, with the term “approaches to learning” defined as teacher ratings of children’s classroom engagement, motivation, and participation.

Interactions with Familiar Adults
A child’s ability to interact competently with familiar adults is important to social competence and the ability to obtain the assistance the child needs. The ability to interact with other adults is important also to school success because children in kindergarten and the primary grades must interact with many adults other than their teachers.

Interactions with Peers
Children who experience greater peer acceptance and positive peer relationships tend to feel more positively about coming to school, participate more in classroom activities, and achieve more in the classroom.
Instruction: Signature Elements Link to this section
Below are signature elements of SFUSD Social-Emotional instruction that students should experience regularly throughout Pre-K as they acquire the social skills, self-awareness, and personal qualities that are interconnected with learning in a classroom.
Building Relationships
Social and emotional learning takes place within the context of relationships. It's important for relationships between the child and teacher are nurtured at the outset. This video shows elements of building positive relationships with new children in our care.

Kimochis
Kimochis is the adopted social and emotional learning curriculum for PK and TK. Teachers are trained in the curriculum and a professional learning community (PLC) is offered to support implementation. PreK instructional coaches are also trained to support implementation.

Conflict resolution
Conflicts are a natural part of early childhood classrooms. Conflicts between children are an opportunity to practice social and emotional skills and develop tools for peaceful resolutions that keep all children physically, emotionally, and socially safe.
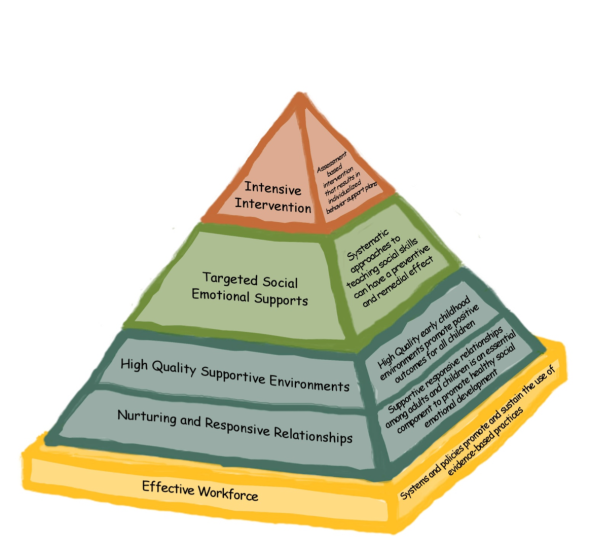
California Collaborative for the Social and Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (CA CSEFEL)
The CA Collaborative for the Social and Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (CA CSEFEL) came from the National Center for Social and Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (CSEFEL). The Teaching Pyramid Approach, developed by CSEFEL, provides a systematic framework that incorporates positive behavior support through promoting social-emotional development, providing support for children’s appropriate behavior, preventing challenging behavior, and addressing problematic behavior. This is the adopted curriculum for the California State Preschool Program.
Materials
Kimochis kits are available to teachers and teams that have completed the 6-hour Kimochis Training. To receive a kit or replacement materials please contact johnckb@sfusd.edu
- If your students are familiar with Kimochis, this Kimochi Feelings Sort activity on Seesaw, designed by an SFUSD teacher, can both give them an opportunity to reinforce identifying their feelings and provide an easy introduction to the Seesaw platform. (Make sure to model it first). For help getting started with Seesaw see the Digital Learning Getting Started Guide for TK, as, your school’s DLeaF, or contact Steve Kesel (KeselS@sfusd.edu).
- Teaching Pyramid Inventory of Practice
- CSEFEL Social Stories
- How to Create a Social Story
- Sometimes I get Mad Social Story
- Six Steps to Resolving Conflict pocket poster
- Problem-Solving Sequence Card
- Visual What Happened Problem Cards
- All Feelings Are Ok, All Behaviors Are Not poster
- Finger Play Conflict Resolution Strategy
Reflective Questions Link to this section
- How are students' developmental needs, communities, and experiences being reflected and honored, or how could they be?
- What opportunities do you see for developing equitable access & demand, inquiry, collaboration, and assessment for learning?
- What are the implications for your own practice? What strengths can you build upon? What will you do first?
Want more?
Standards
CA PTKLF Social and Emotional Development - The Preschool/Transitional Kindergarten Learning Foundations (PTKLF) in the domain of Social and Emotional Development describe the social and emotional competencies children can demonstrate and develop through their early learning experiences. The PTKLF provide guidance on the wide range of social and emotional knowledge and skills that children age three to five and a half typically attain when attending a high-quality early education program.
More Resources
This Seesaw Activity was designed by an SFUSD teacher, students sort their ‘Kimochi feelings’ into two bags.
Moving From Praise to Acknowledgement
CA Teaching Pyramid Classroom Materials
Contact
Michele Callwood, PBIS Coach EED - callwoodm@sfusd.edu
Jetta Jacobson, Instructional Coach EED - jacobsonj@sfusd.edu
Barbara Johnck, Program Administrator of PBIS Support - johnckb@sfusd.edu
Crystal Hawkins, Program Administrator of Shoestrings - hawkinsc@sfusd.edu
This page was last updated on May 2, 2025

